Sustainable development is a task for all of humanity. This is why at KIT we create and impart knowledge for the society and the environment and are actively committed to sustainable development. We shape a sustainable future through innovative cutting-edge research on the topics of climate protection, resource conservation and other aspects of sustainable living and business, through research-oriented teaching and the transfer of knowledge and solutions to business, politics and civil society. We also implement the knowledge and solutions gained at KIT in our own actions.
As a strategic cross-cutting issue, sustainability is part of KIT's DNA. We are continuously implementing measures to strengthen it step by step.
sprungmarken_marker_35358
Collective action at KIT enables us to take responsibility for sustainable development and to contribute to future-oriented science and its implementation in society through effective measures. This is supported by the entire Executive Board.
Prof. Kora Kristof, Vice President Digitalization and Sustainability
Strategy and vision
Our vision?
A sustainable KIT, shaped together with all members of KIT, which contributes significantly to accelerating the path towards sustainability.
Strategy
- In 2022, KIT included sustainability as a separate field of action in the KIT 2025 Strategy and established a new portfolio "Digitalization and Sustainability" in 2023 under the leadership of Vice President Professor Dr. Kora Kristof.
- A series of structural measures had already been defined in the 2022 - 2026 structure and development plan (SEP).
- Our Sustainability Strategy provides for net greenhouse gas neutrality by 2030 and many other targets.
- We are guided by the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the sustainability strategies of the federal government and the federal state of Baden-Württemberg.
- Together with the other Helmholtz Centers, we have formulated the "Helmholtz Association's commitment to sustainable development" and stand behind it.
- We also consider the interface between digitalization and sustainability to be important and are conducting research and developing solutions to ensure that the highly dynamic digital transformation is sustainable from the beginning and to accelerate the sustainability transformation through digital solutions.
- Together we achieve our goals: We prepare trend-setting decisions together with the members of KIT and collaborate actively with local, national and international players.
Governance
- Under the leadership of Vice President Professor Dr. Kora Kristof, the Digitalization and Sustainability portfolio centrally coordinates sustainability activities at KIT in order to further increase the visibility and effectiveness of research, teaching, transfer, technologies as well as the ability to engage in dialogue with society on climate protection, resource conservation and other aspects of sustainable development.
- The Vice President is supported by the Sustainability Office (SO). As the central office for the sustainability management work of all stakeholders, it pushes KIT’s sustainable development in a pluralistic, integrated approach.
- In 2021, the Round Table on Sustainability was established as an internal discussion platform to sharpen sustainability topics from science and administration. The committee structure on sustainability is currently being further developed as part of the Basis Project Sustainability.
Strategic projects
Basic Project Sustainability (duration: 2023-2025): According to the motto "Together.Sustainable.KIT", employees and students actively shape sustainability at KIT in a broad participartory process in research, higher education, transfer, as well as in our own organization – from everyday study and work life to infrastructures. Further information can be found on the project website (visible only on the intranet)
Digitalization and Sustainability Interface Project (duration: 2024-2025): The aim of the project is to identify important potentials at the interface of these two central transformations in a participation-oriented manner. Ideas are developed together with students and employees to combine digital change and sustainability in a useful way. Further information can be found on the project website (visible only on the intranet)
Energy
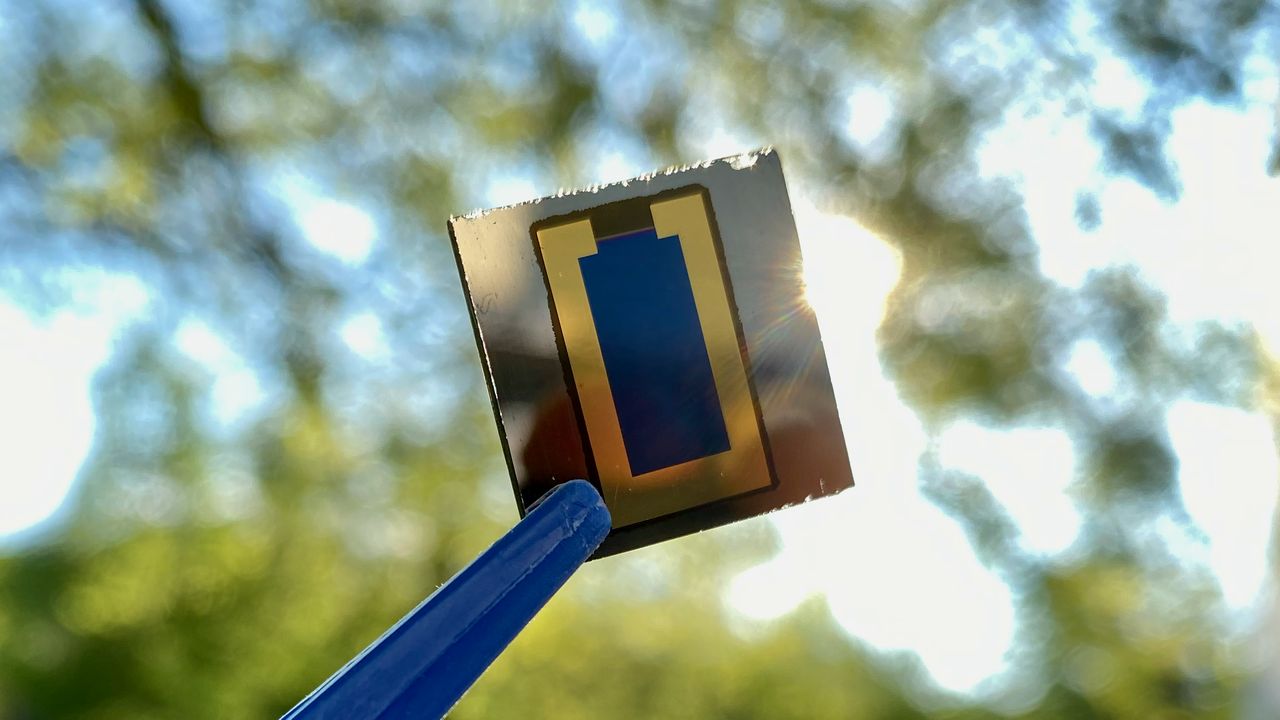
KIT Energy Center
The KIT Energy Center focuses on innovative and sustainable energy solutions aimed at accelerating the transition to environmentally friendly energy systems and meeting global energy needs sustainably.
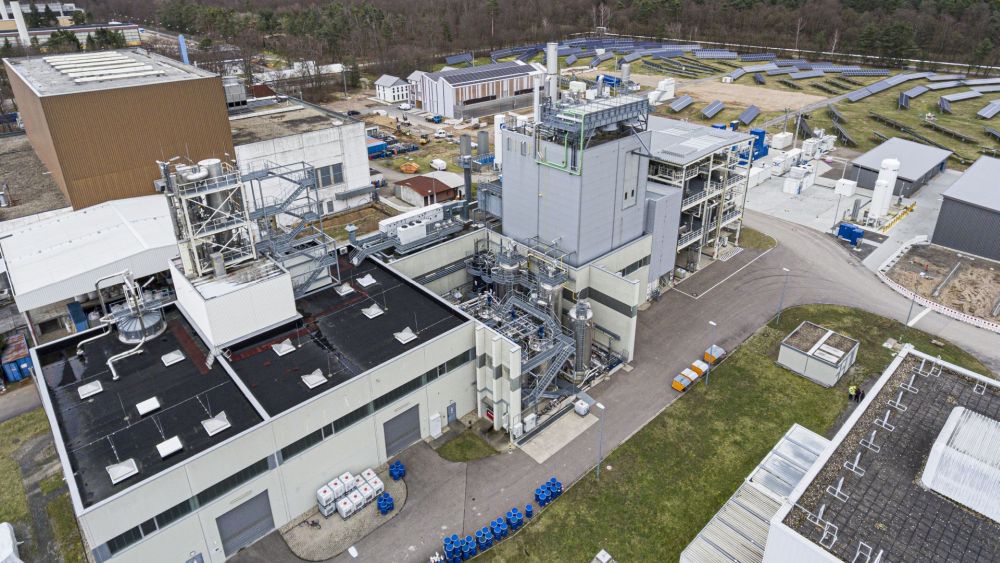

Energy Lab
In Europe's largest research infrastructure for renewable energies the intelligent networking of environmentally friendly energy generators and storage methods is being investigated.
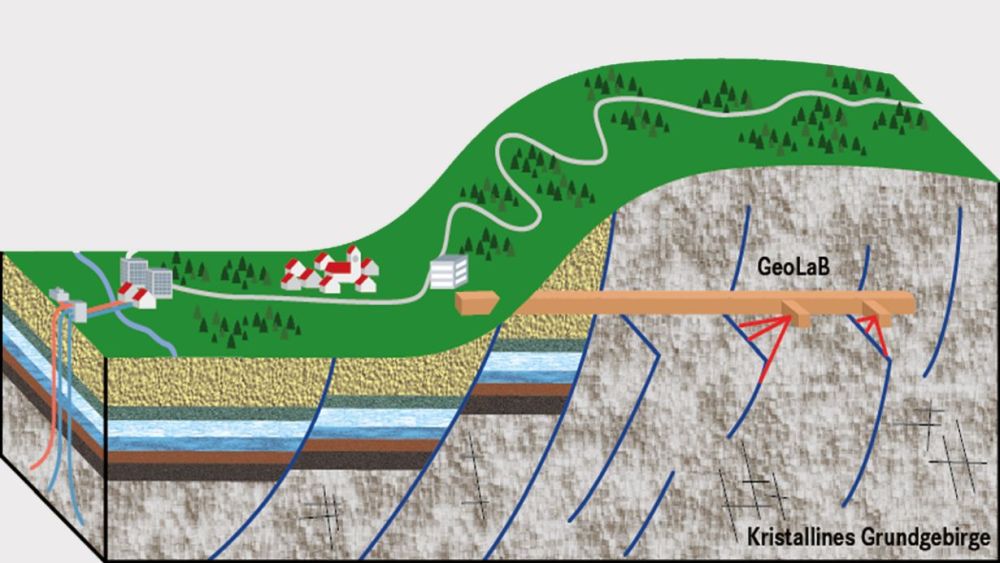
GeoLaB – Reserach lab geothermal energy
This research project will use an underground research laboratory to investigate how geothermal energy can be sustainably exploited and used for a secure and sustainable energy supply.
Mobility
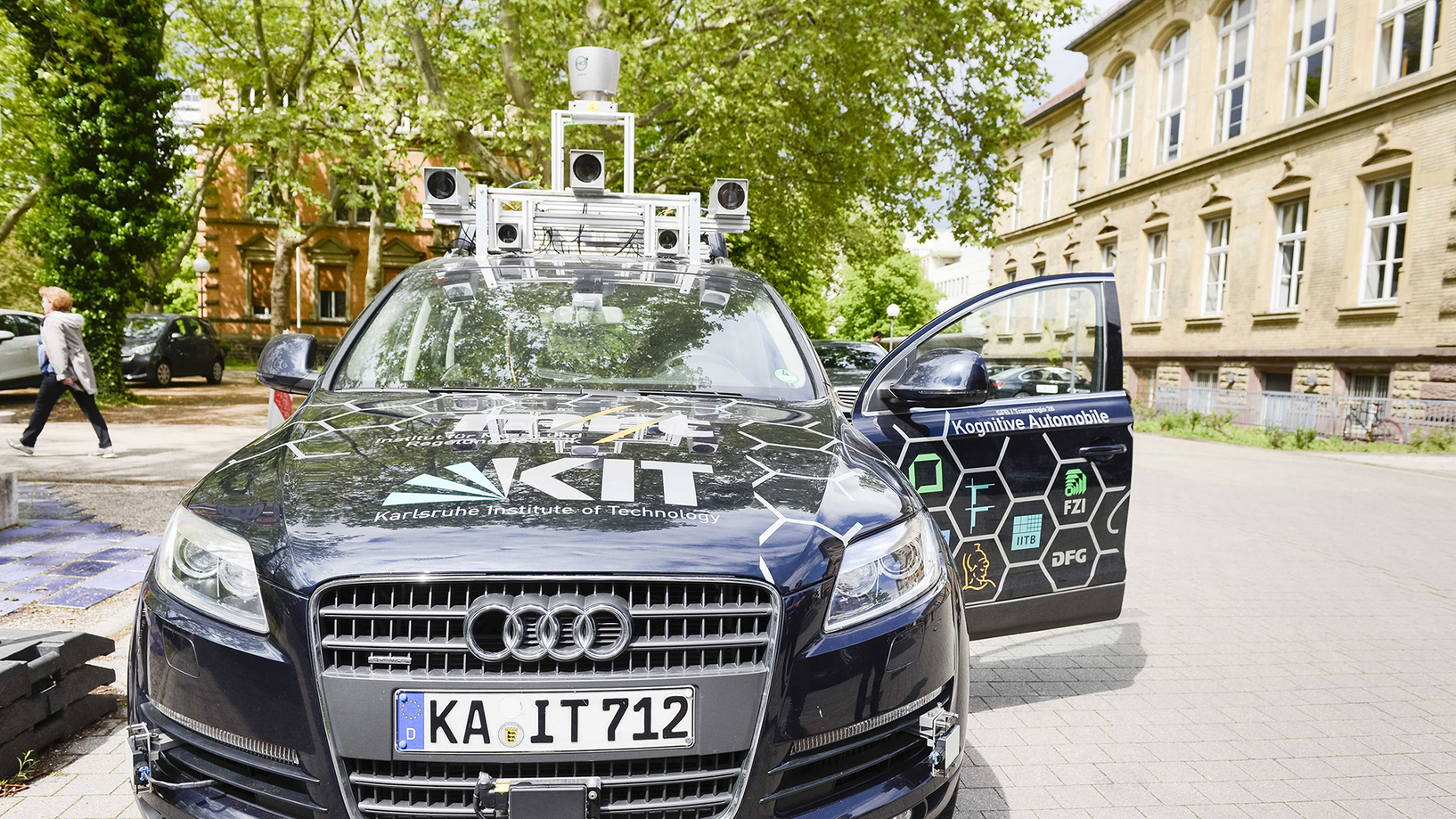

KIT Mobility Systems Center
The KIT Mobility Systems Center conducts research on sustainable mobility. Examples include low-emission vehicles, traffic planning and the integration of digital technologies and solutions for new sustainable mobility systems to improve traffic efficiency.

C2CBridge - Country to City Bridge
Researchers investigate innovative mobility solutions to improve the connection between rural and urban areas and to promote sustainable transportation concepts.
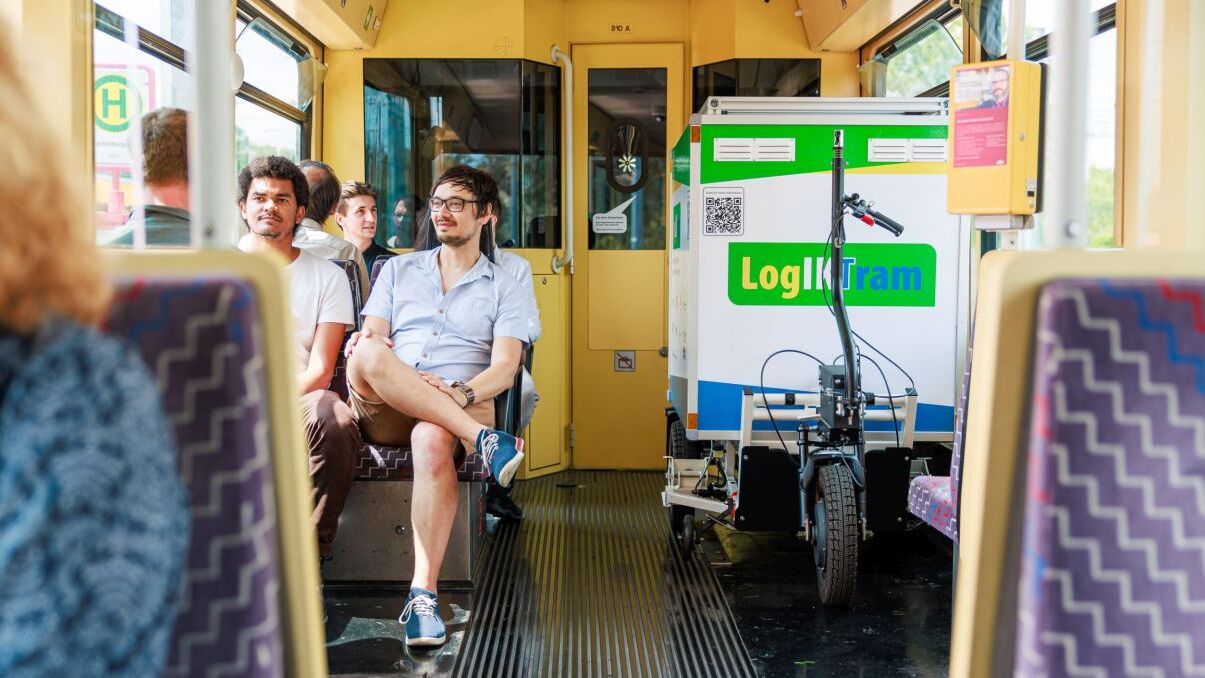

LogIKTram
The LogIKTram joint project develops an innovative, environmentally friendly logistics concept for future freight transport in streetcar and light rail vehicles.
Climate and environment

KIT Climate and Environment Center
The KIT Climate and Environment Center develops basic and applied knowledge on climate and environmental change as well as nature-based and technological solutions for safeguarding the natural basis of life and shaping the living environment.

KARLA
The Karlsruhe Real-World Laboratory for Sustainable Climate Protection (KARLA) develops and tests practical, innovative solutions for integrating sustainability into everyday life and for local climate protection.

Changing Earth - Sustaining our Future
In this Helmholtz research program, scientists are researching climate change, the decline in biodiversity and geological risks, among other things.
Resource conservation and circular economy

Circular Factory for the Perpetual Product
This collaborative research center investigates innovative approaches to creating products that can be reused through intelligent circular systems. Digital technologies are used to optimize life cycles.

Concrete without climate-damaging emissions
Concrete without climate-damaging emissions: The "Zero Emission Circular Concrete" project is developing a cycle that converts old concrete into CO2-neutral and resource-efficient concrete.

Sustainable materials
At the KIT Center Materials in Technical and Life Sciences (MaTeLiS) more sustainable materials that are convincing in application and at the same time as sustainable as possible for the environment and society are investigated.
Urban transformation

Urban Research at KIT
KIT contributes to research and shaping the city of the future with a holistic approach that combines expertise in engineering, humanities, social and environmental sciences.

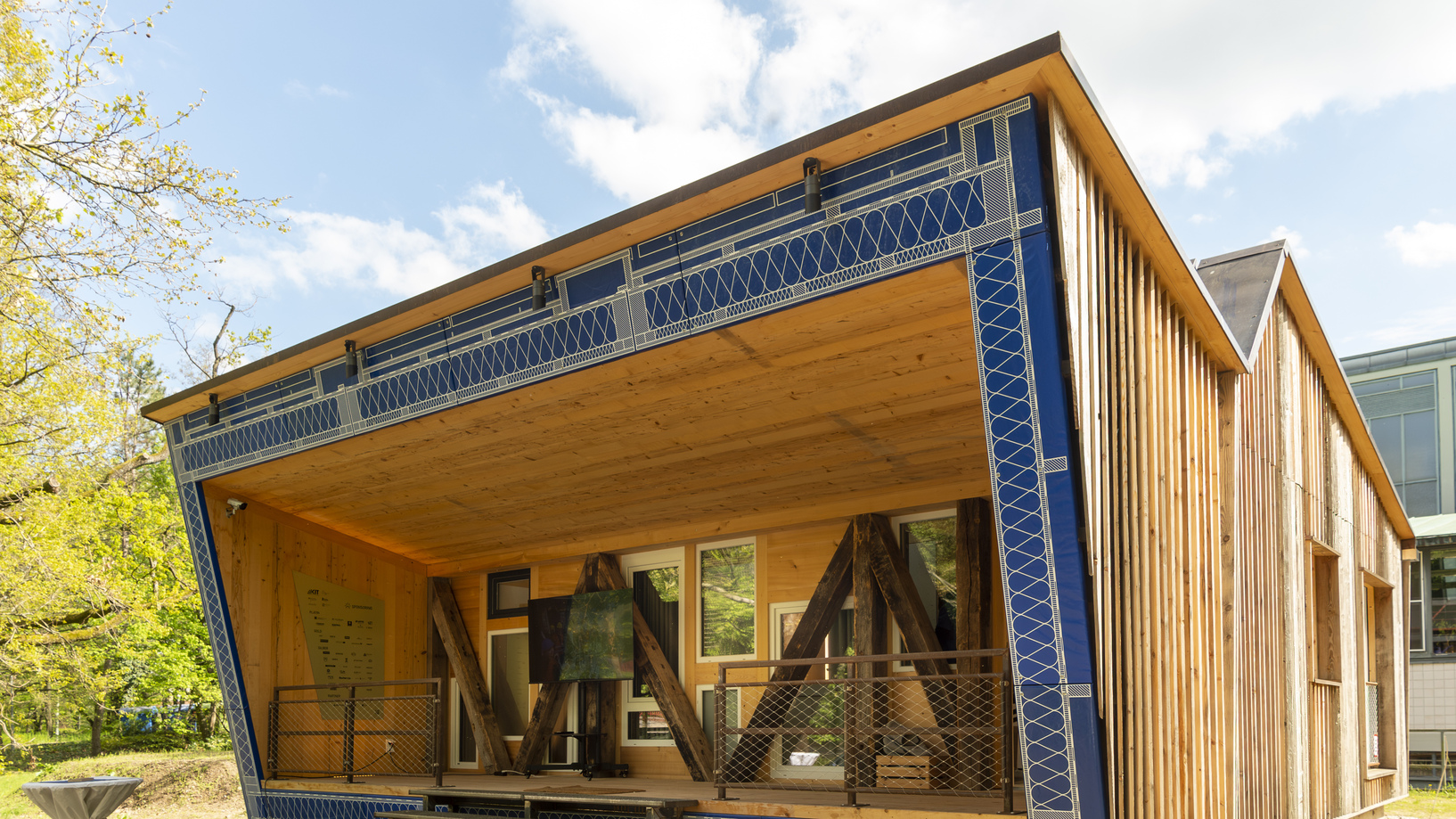
Sustainable construction
The Chair of Sustainable Construction conducts research in the field of circular construction and has been able to construct several demonstration buildings using new methods and construction methods. Other professorships are also dedicated to this topic (e.g. circular wood construction, technologies for climate-friendly buildings and urban districts, and energy-efficient building technology).

District Future – Urban Lab
In the District Future – Urban Lab, scientists work together with society to test and research sustainable urban development.
Digitalization and sustainability

Data Science in Climate and Environmental Research
In the KIT Climate and Environment Center environmental phenomena using artificial intelligence methods are investigated.

HoreKA
KIT's supercomputer is not only one of the most energy-efficient in the world, but also features an innovative hot water cooling system, which makes its operation more sustainable and environmentally friendly.

MobileCity-App
This app allows players to shape ecologically and financially sustainable mobility in cities and municipalities. It is the result of the MobileCityGame research project and was awarded the German Mobility Prize in 2023.
Researching sustainably

Framework for reflection on research with societal responsibility
The reflection framework supports researchers in shaping their research process responsibly.

KIT Test Field for Energy Efficiency and Grid Stability in Large Research Infrastructures (KITTEN)
The KIT test field KITTEN combines the Energy Lab with the test facility for accelerator technologies KARA to jointly develop how large-scale research facilities can be operated more efficiently and sustainably using KARA as an example and then validate this experimentally under real conditions.
Research infrastructures
As a research university in the Helmholtz Association, KIT operates large research infrastructures at which scientists not only research various issues related to sustainability, but also take advanatage of the opportunities offered by the sustainable operation of research infrastructures integrated into the KIT campus.
Real-world laboratory research
Another special feature at KIT is real-world laboratory research. KIT scientists conduct transdisciplinary research in various real-world labs. This means that, together with industry, public administration and civil society, sustainable solutions for complex issues are being developed, tested and brought to a wider audience from the outset in collaboration with practitioners.
Education for Sustainable Development (ESD)
ESD is an education approach that enables people to think and act in a sustainable way and provides them with the necessary skills. Our commitment to ESD has been recognized several times: In 2018, KIT was awarded as a place of learning for sustainable development. In 2021, the Spring Academy Sustainability received the Baden-Württemberg Teaching Award for ESD. In 2022, KIT was recognized as a learning environment for ESD. Further information can be found here.
Courses on Education for Sustainable Development (ESD)

Certificate Sustainable Development
The Certificate Sustainable Development offers a compact insight into sustainability topics - with a scientific approach and the opportunity to reflect on complex, interlinked social and ecological issues.

Supplementary Studies on Science, Technology and Society
In the supplementary studies, students can explore and understand interdisciplinary perspectives on the interactions between science, technology and their social significance and deal more intensively with sustainability in their individual focus.

Supplementary Studies on Sustainable Development
The supplementary study program of the FORUM imparts application-oriented knowledge, sound theories and methods for reflective and sustainable action in studies, work and society.
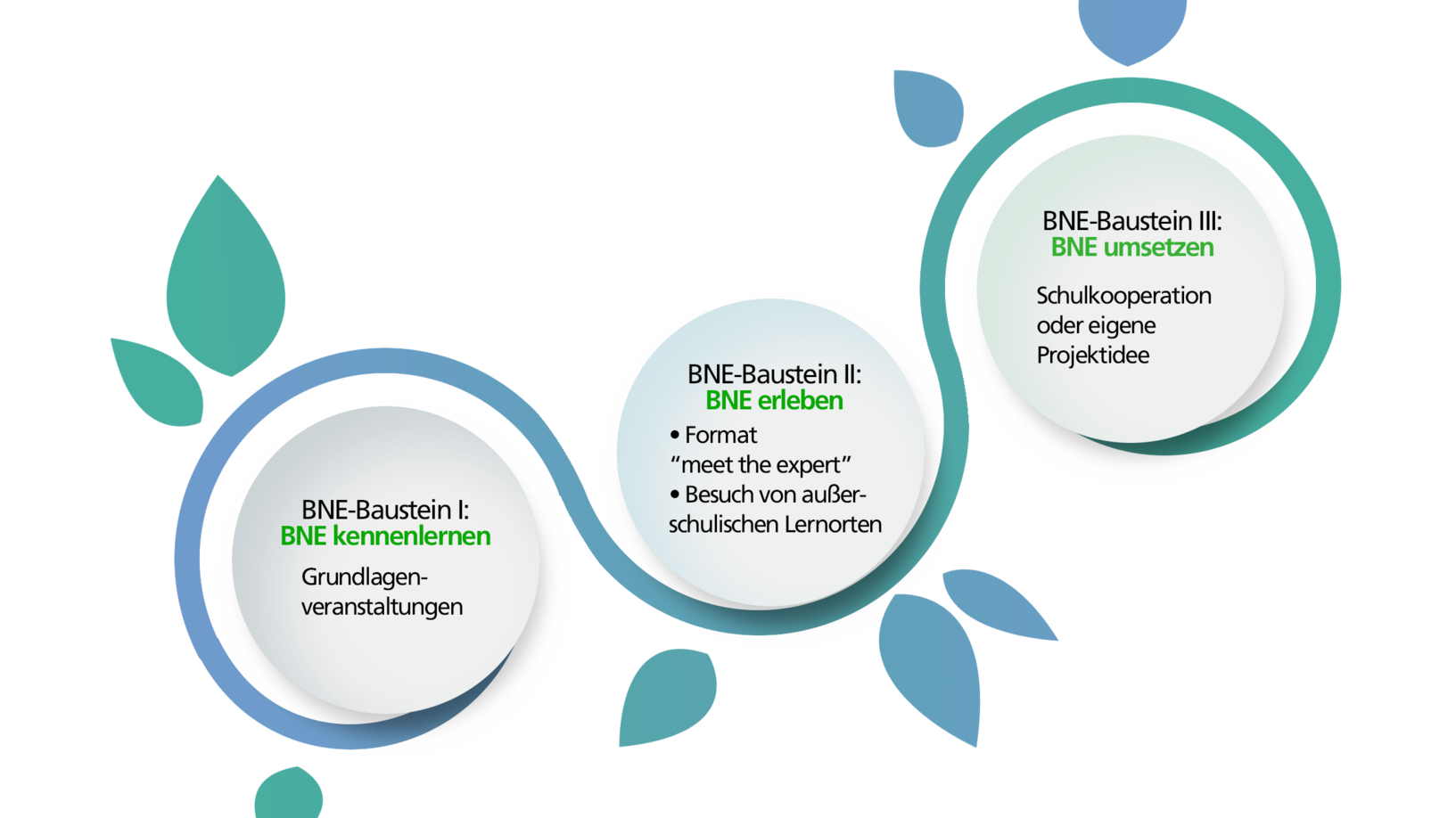
Certificate "Shaping schools sustainably"
Starting in the winter semester 2024/25, the Center for Teacher Education offers the certificate "Shaping schools sustainably", in which the basics of ESD are taught, own project ideas are developed and the exchange with extracurricular learning locations and ESD experts is strengthened.

Spring Acadcemy Sustainability
The annual interdisciplinary project week of the FORUM is aimed at students and, with the public parts, at anyone interested in sustainable development.

KAT #climateChallenge
This innovative educational format aims to motivate people to reduce their personal CO2 footprint and work towards greater and holistic climate protection.

ENZo Talks
The KIT graduate school "Enabling Net Zero" (ENZo) regularly organizes lectures and panel discussions on sustainability topics with the opportunity for professional input and exchange.

Lecture series "Sustainable Construction"
Each winter semester the architecture professorships offer a lecture series on "Sustainable Construction", which adresses the history, state of the art and alternative futures within the theme.

School of Transformation
The joint pilot project of the Karlsruhe Transformation Center for Sustainability and Cultural Change (KAT) and the House of Comptenece (HoC) offers workshops and other courses for students and interested parties who want to actively (co-)shape change.

ARRTI lectures and seminars
The Academy for Responsible Research, Teaching and Innovation (ARRTI) offers courses on issues of responsibility every semester - regularly including a responsibility perspective on sustainability topics.


Student labs
Student labs at KIT offer pupils the opportunity to experience science and technology at first hand through practical experiments and projects - for example on the topics of the environment, energy and STEM moves sustainably.

Science camps for young people
At the science camps, young people have the opportunity to carry out their own projects and research, look over the shoulders of scientists and slip into the role of a researcher themselves - for example on the topics of climate and environment, geothermal energy und energy.
Green course catalog
The Green Course Catalog of the green-alternative student group (GAHG) provides an overview of courses related to sustainable development
Criteria are currently being developed to make sustainability-related courses visible in the official KIT course catalog.
International courses
- EPICUR: In the European university alliance EPICUR, KIT students have the opportunity to attend courses offered by all universities - also in the field of Sustainable Transformation. From April 2025, the EPICUR Hub Sustainable Transformation will serve as a virtual center for transnational scientific collaboration and research training, interdisciplinary engagement and cross-institutional collaboration.
- The FORUM offers the “Certificate Sustainable Development”. There are several courses per semester.
- Erasmus+ grant for environmentally friendly travel: Students who travel to their Erasmus destination without a car or plane receive additional financial support.
Our dialog formats on sustainability topics
- Science Week
- KIT in the Town Hall
- Knowledge Weeks
- Spring Academy Sustainability
- KIT Climate and Environment Lecture
- Environment Brain Bites and Climate Brain Bites
- Karlsruhe Environmental Impulses
You can find an overview of all events in the events calendar.

Karlsruhe Transformation Center for Sustainability and Cultural Change (KAT)
KAT combines research, education, consulting and process support to promote the transition to a sustainable culture and overcome social challenges.

Innovation Campus Future Mobility
Scientists from the University of Stuttgart and KIT are working with partners from industry and society to develop innovative and sustainable solutions for the mobility of tomorrow.

Sustainability Innovation Campus
Scientists from the University of Freiburg and KIT are working with partners from society, business and politics to implement projects in the fields of climate protection, wellbeing and resource conservation.

South German Climate Office
At the South German Climate Office, one of four regional climate offices of the Helmholtz Association, researchers prepare complex scientific data on climate change in an understandable way and promote dialog between climate research and society.
Sustainability from everyday study and work life to infrastructures
We are aiming for net greenhouse gas neutrality by 2030 and other sustainability goals and therefore place a strong focus on ecological sustainability without losing sight of social and economic aspects. Sustainability is a joint task that we tackle and implement together with all members of KIT. Many initiatives arise from the commitment of employees and students.
Sustainability in everyday study and work life
We want to enable both students and employees to shape their everyday lives as sustainable as possible.
- Media production: We have been using sustainable paper with the Bauer Engel standard since 2017. We also use recyclable materials for displays and signage at events.
- Procurement: We take into account the Act on Corporate Due Diligence Obligations in Supply Chains in our guidelines and thus responsible corporate practices along the entire supply chain. We also promote the reuse of old office furniture.
Mobility
Mobility has a major influence on the environmental impact of KIT - at the same time, university and research operations are not possible without mobility. We are constantly working on expanding the options for sustainable mobility.
- The mobility portal provides information on sustainable mobility solutions such as cycling, public transport (incl. shuttle & Deutschlandticket) and car sharing.
- E-mobility: More and more electric vehicles are being used in the vehicle fleet. Several charging stations are available on KIT grounds for employees, guests and company vehicles.
- Bicycle traffic: KIT aims to increase the use of bicycles and the mode share of cycling of employees and students through various measures. These include company bicycles, a mailing list for cyclists, pump and repair stations and participation in the annual STADTRADELN.
- Business trips: Business trips, especially air travel, cause high greenhouse gas emissions. KIT employees can obtain important information on climate-friendly travel options from the Personnel Service. Additional information can be found in the handout on climate-friendly business trips at scientific institutions from the Karlsruhe Real-World Lab Sustainable Climate Protection (KARLA).
Catering and events
- Sustainability also plays an important role in daily catering, both at the Studierendenwerk Karlsruhe and at the campus gastronomy on the Campus North. This includes, for example, the procurement of food from regional and sustainable sources, the expansion of organic offerings, the reduction of food waste and the integration of more plant-based dishes into the menus.
- With our guideline "Sustainable Event Management at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology", we focus on sustainable event organization. We strive for the "Green Event BW" seal for all central events.
Energy transition and climate protection
- With almost 33,000 students and employees, KIT is one of the largest institutions in Karlsruhe with a correspondingly high energy consumption. Detailed information on the annual consumption values can be found in the KIT annual report.
- Green electricity: KIT's urban campus areas (South/West/East Campus) have been using green electricity since 2016 and KIT has also been using green electricity with guarantees of origin at the North Campus since 2025.
- Photovoltaics: We are pursuing ambitious goals for the expansion of photovoltaics. Solar systems with a total output of 2 megawatt peak have been installed at KIT and a further 2 megawatt peak are planned for 2025.
- Heat supply: The urban campus areas are largely supplied by municipal district heating from industrial waste heat. At the North Campus, the Gas Engine Test Laboratory (GEL) supplies electricity and heat to the supply networks of the North Campus at KIT as a combined heat and power plant. In order to achieve the goal of climate neutrality, various options for defossilizing KIT's heat supply are currently being investigated in an internal KIT-funded study.
- LED lighting: LED lighting was installed with funding from the Helmholtz Association in order to reduce energy consumption.
- Energy-saving tips: The Facility Management Business Unit has compiled tips on how everyone at KIT can save energy.
Campus and buildings
-
Building infrastructures: With the takeover of building owner status in 2024, KIT as a state university is now also responsible for construction and renovation projects on the South, East and West Campuses in addition to its responsibility for the North Campus, which offers more room for maneuver. Renovation and (replacement) new construction projects are managed by the Business Unit Planning and Construction Projects (PB). Construction measures are certified with the sustainability seal "Assessment System for Sustainable Building" (for new buildings consistently with the silver standard). In 2023, the two InformatiKOM buildings, which were implemented with the Klaus Tschira Foundation in accordance with the silver standard, went into operation. KIT is also implementing a particularly sustainability-oriented building concept for the Karlsruhe Center for Optics and Photonics, which is currently under construction.
-
Green areas and climate change adaptation: We are redesigning green maintenance at KIT to promote biodiversity and counter the effects of climate change. This includes, for example, less frequent mowing, taking vegetation periods and weather into account. To promote biodiversity, so-called dead grass strips, i.e. deliberately unmown areas, have been used. In addition, green cuttings, compost and woody plants are used on green spaces to create habitats and winter quarters for animals.
Facts and Figures
Status as of 2023, Source: KIT Annual Report
1Real CO2 emissions (CO2 equivalents incl. upstream chains) from the energy supply of all KIT sites in tons per year [t CO2eq/a] with dual reporting for electricity in accordance with the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP)
2excl. grid losses and without heat demand from thermal cooling systems
Participate and Connect
Sustainability is a joint task that is made possible by the commitment of stakeholders at all levels. We are always happy to welcome people who want to get involved and enrich our networks.
KIT memberships in sustainability networks
Karlsruhe Climate Pact
As part of the Karlsruhe Climate Pact, KIT works with all seven Karlsruhe universities and the city of Karlsruhe on climate protection measures. The Climate Pact was created on the initiative of KIT's Karlsruhe Real-World Laboratory for Sustainable Climate Protection (KARLA) with the aim of utilizing synergies and combining expertise.
Helmholtz Asscociation
Helmholtz Sustainability Working Group: In order to actively promote the topic of sustainability within the Helmholtz Association, since April 2018, the Helmholtz Sustainability Working Group has been dealing with a wide range of issues relating to facets of sustainability at an economic, social and ecological level. The Helmholtz Sustainability Working Group regularly organizes the Helmholtz Sustainability Summit.
Society for Transdisciplinary and Participatory Research
KIT is an institutional and founding member of the Society for Transdisciplinary and Participatory Research (GTPF). The association connects researchers and teachers as well as practice partners and promotes transdisciplinary and participatory research and teaching.
Initiatives and working groups
- Sustainability working group of the Staff Council (visible only on the Intranet)
- Sustainability Working Group of the KIT library
- Scientists for Future
As well as other initiatives and working groups at the institute level
Student activities
Studierendenwerk
Vice President Digitalization and Sustainability





