The effect is known from the smart phone: Sun is reflected by the display and hardly anything can be seen. In contrast to this, the glasswing butterfly hardly reflects any light in spite of its transparent wings. As a result, it is difficult for predatory birds to track the butterfly during the flight. Researchers of KIT under the direction of Hendrik Hölscher found that irregular nanostructures on the surface of the butterfly wing cause the low reflection. In theoretical experiments, they succeeded in reproducing the effect that opens up fascinating application options, e.g. for displays of mobile phones or laptops.
The results are published in the current issue of Nature Communications: DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7909.
Transparent materials such as glass, always reflect part of the incident light. Some animals with transparent surfaces, such as the moth with its eyes, succeed in keeping the reflections small, but only when the view angle is vertical to the surface. The wings of the glasswing butterfly that lives mainly in Central America, however, also have a very low reflection when looking onto them under higher angles. Depending on the view angle, specular reflection varies between two and five percent. For comparison: As a function of the view angle, a flat glass plane reflects between eight and 100 percent, i.e. reflection exceeds that of the butterfly wing by several factors. Interestingly, the butterfly wing does not only exhibit a low reflection of the light spectrum visible to humans, but also suppresses the infrared and ultraviolet radiation that can be perceived by animals. This is important to the survival of the butterfly.
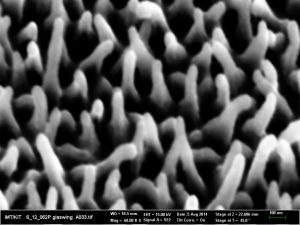
Irregularity of the size and distribution of nanostructures on the surface of the butterfly wing causes low reflection of light at all view angles. (Photo: Radwanul Hasan Siddique, KIT)
For research into this so far unstudied phenomenon, the scientists examined glasswings by scanning electron microscopy. Earlier studies revealed that regular pillar-like nanostructures are responsible for the low reflections of other animals. The scientists now also found nanopillars on the butterfly wings. In contrast to previous findings, however, they are arranged irregularly and feature a random height. Typical height of the pillars varies between 400 and 600 nanometers, the distance of the pillars ranges between 100 and 140 nanometers. This corresponds to about one thousandth of a human hair.
In simulations, the researchers mathematically modeled this irregularity of the nanopillars in height and arrangement. They found that the calculated reflected amount of light exactly corresponds to the observed amount at variable view angles. In this way, they proved that the low reflection at variable view angles is caused by this irregularity of the nanopillars. Hölscher’s doctoral student Radwanul Hasan Siddique, who discovered this effect, considers the glasswing butterfly a fascinating animal: “Not only optically with its transparent wings, but also scientifically. In contrast to other natural phenomena, where regularity is of top priority, the glasswing butterfly uses an apparent chaos to reach effects that are also fascinating for us humans.”
The findings open up a range of applications wherever low-reflection surfaces are needed, for lenses or displays of mobile phones, for instance. Apart from theoretical studies of the phenomenon, the infrastructure of the Institute of Microstructure Technology also allows for practical implementation. First application tests are in the conception phase at the moment. Prototype experiments, however, already revealed that this type of surface coating also has a water-repellent and self-cleaning effect.
In close partnership with society, KIT develops solutions for urgent challenges – from climate change, energy transition and sustainable use of natural resources to artificial intelligence, sovereignty and an aging population. As The University in the Helmholtz Association, KIT unites scientific excellence from insight to application-driven research under one roof – and is thus in a unique position to drive this transformation. As a University of Excellence, KIT offers its more than 10,000 employees and 22,800 students outstanding opportunities to shape a sustainable and resilient future. KIT – Science for Impact.

