Geckos outclass adhesive tapes in one respect: Even after repeated contact with dirt and dust do their feet perfectly adhere to smooth surfaces. Researchers of the KIT and the Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, have now developed the first adhesive tape that does not only adhere to a surface as reliably as the toes of a gecko, but also possesses similar self-cleaning properties. Using such a tape, food packagings or bandages might be opened and closed several times. The results are published in the “Interface“ journal of the British Royal Society. DOI: rsif.2013.1205
When moving forwards, the gecko‘s toes drag across a part of the surface. As a result of this lateral friction contact, larger dirt particles are removed. Smaller particles deposit among the setae on the sole and in the skinfolds below. In an experiment, the researchers have proved that both mechanisms provide for 95% of the self-cleaning effect. “This effect is determined by the ratio between particle size and setae diameter“, Dr. Hendrik Hölscher of KIT’s Institute of Microstructure Technology (IMT) says.
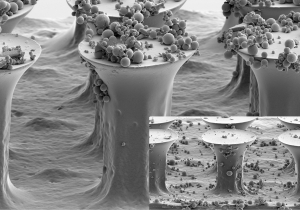
Glass spheres among microhairs that are mushroom-shaped to improve adhesive force. (SEM: Michael Röhrig, KIT)
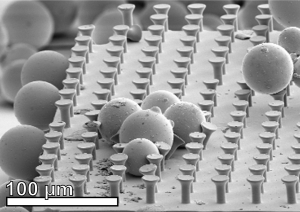
For their experiments, the scientists used elastic microhairs of variable size. Instead of dirt particles, they employed glass spheres of micrometer size (10-6 meters) and distributed them on a smooth plate. To simulate the steps made by a gecko, they pressed an artificial adhesive tape covered by microhairs onto the plate, shifted it laterally, and lifted the tape off again. This “load-drag-unload“ cycle was repeated several times. In parallel, adhesive force was measured.
When the diameter of the spheres exceeded that of the microhairs, the adhesive force disappeared after the first contact (”load“) – as in case of an ordinary adhesive tape. After eight to ten test cycles, however, the gecko-inspired adhesive tape reached 80 to 100 percent of its original power again. “In the long term, this effect might be used to develop a low-cost alternative to hook and loop fasteners,“ Hölscher says. “Such a tape might be applied in the sports sector, in medicine, automotive industry or aerospace technology,“ Metin Sitti, Professor of the Carnegie Mellon University, adds.
When the size of the spheres was smaller than the diameter of the microhairs, the researchers succeeded in restoring one third of the original adhesive force only. “For the perfect gecko-inspired adhesive tape, we therefore need fibers in the nanometer range (10-9 meters), which are smaller than most dirt particles“, Dr. Michael Röhrig, IMT scientist, emphasizes. The skinfolds of the gecko have already been reproduced by wide grooves between narrow rows of hair. They offer enough space for the fine dust to deposit. Tests using real dirt particles of variable shape and size and particles made of various materials are planned to be carried out in the near future.
Mengüç Y, Röhrig M, Abusomwan U, Hölscher H, Sitti M. 2014 Staying sticky: contact self-cleaning of gecko-inspired adhesives.
J. R. Soc. Interface 20131205.
http://rsif.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/11/94/20131205